Bassett Collection of Stereoscopic Images of Human Anatomy
Exploration of the basal aspects of the medulla, pons and cerebellum
Origins of cranial nerves V-XII
Image #28-3
KEYWORDS: Brain, Cerebellum, Medulla, Peripheral nervous system.
Creative Commons
Stanford holds the copyright to the David L. Bassett anatomical images and has assigned Creative Commons license Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International to all of the images.
For additional information regarding use and permissions, please contact the Medical History Center.
Exploration of the basal aspects of the medulla, pons and cerebellum
Origins of cranial nerves V-XII
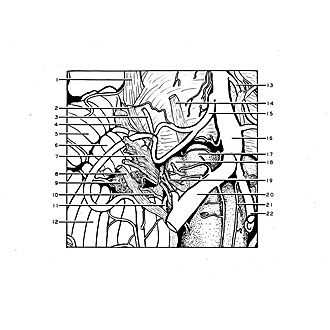
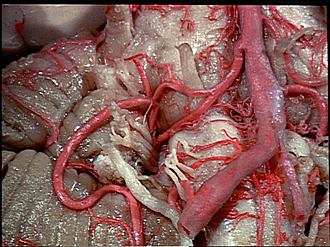
In this view of the inferior surface of the right half of the brain stem the origins of cranial nerves V-XII are seen in relation to the arteries in the area. Several bulbar rootlets join the ascending spinal root of the accessory nerve. The tuft of choroid plexus (9), visible just lateral to nerves IX and X, protrudes from the lateral aperture of the fourth ventricle. Note the right internal auditory artery (3) arising from the anterior inferior cerebellar artery, the left (13) arising from the basilar artery. Disparity in the size of the two vertebral arteries, as seen here, is not uncommon. Numerous small arteries enter the medulla. Pia mater is left intact in most places. A small filament of the glossopharyngeal nerve (7) is displaced across the anterior inferior cerebellar artery.
- Trigeminal nerve (V)
- Facial nerve (VII)
- Internal auditory artery
- Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
- Quadrangular lobule of cerebellum
- Flocculus
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX) and vagus nerve (X)
- Accessory nerve (XI)
- Choroid plexus fourth ventricle
- Accessory nerve (bulbar rootlet)
- Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
- Cerebellar tonsil (ventral paraflocculus)
- Internal auditory artery
- Abducens nerve (VI)
- Anterior inferior cerebellar artery
- Basilar artery
- Pyramid (medulla oblongata)
- Olive
- Hypoglossal nerve (XII)
- Vertebral artery right
- Anterior spinal artery
- Vertebral artery left