Bassett Collection of Stereoscopic Images of Human Anatomy
Dissection of anterolateral abdominal wall
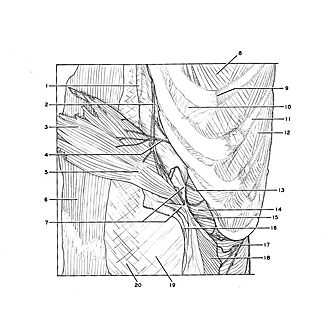
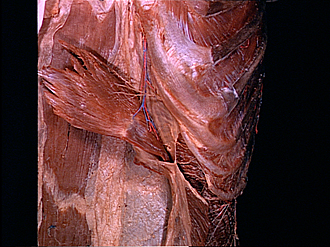
Relation of transversus abdominis muscle to sheath of rectus below costal margin
Image #134-4
KEYWORDS: Muscles and tendons.
Creative Commons
Stanford holds the copyright to the David L. Bassett anatomical images and has assigned Creative Commons license Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International to all of the images.
For additional information regarding use and permissions, please contact the Medical History Center.
Dissection of anterolateral abdominal wall
Relation of transversus abdominis muscle to sheath of rectus below costal margin
The left rectus muscle has been detached from its origin and reflected medially. The layers which comprise its sheath have been separated from each other near the lateral border of the muscle. The aponeurosis of the internal oblique (7) contributes to the anterior as well as to the posterior lamina of the sheath at this level. Anteriorly it fuses with the aponeurosis of the external oblique (16). The transversus muscle (14) passes posterior to the aponeurosis of the internal oblique to become aponeurotic approximately midway in its course behind the rectus muscle.
- Xiphoid process
- Superior epigastric artery
- Left rectus abdominis muscle (reflected)
- Intercostal nerve VII (branch to rectus muscle)
- Tendinous inscriptions
- Right rectus abdominis muscle (sheath opened)
- Sheath of rectus abdominis muscle (pointers on posterior and anterior lamina derived from aponeurosis of internal oblique)
- Internal intercostal muscle
- Costochondral junction
- Interchondral joint
- Rib VII
- External intercostal muscle
- Intercostal nerve VIII
- Transversus abdominis muscle
- Aponeurosis of Internal oblique muscle
- External oblique muscle (cut across and reflected)
- Intercostal nerve X
- Internal oblique muscle (cut across)
- Sheath of rectus abdominis muscle (anterior layer)
- Linea alba