Bassett Collection of Stereoscopic Images of Human Anatomy
Dissection of male pelvis from a lateral approach
External muscles and ligaments at neck of bladder; tendinous arch of pelvic fascia, viewed from above
Image #171-1
KEYWORDS: Muscles and tendons, Urinary tract.
Creative Commons
Stanford holds the copyright to the David L. Bassett anatomical images and has assigned Creative Commons license Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International to all of the images.
For additional information regarding use and permissions, please contact the Medical History Center.
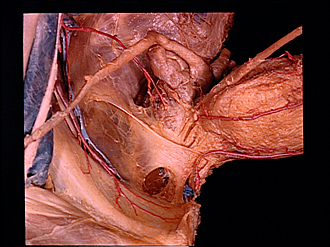
Dissection of male pelvis from a lateral approach
External muscles and ligaments at neck of bladder; tendinous arch of pelvic fascia, viewed from above
The bladder and prostate have been pulled to the left to expose bands of smooth muscle alongside the neck of the bladder which form the m. pubovesicalis (24) and which continue anteriorly into the medial puboprostatic ligament (26). Laterally, the thickened part of the pelvic fascia known as the tendinous arch of the pelvic fascia (25) is seen to be attached to the prostate and neck of the bladder by the lateral puboprostatic ligament (16, upper pointer). The lateral ligament of the bladder, consisting of fibrous tissue and smooth muscle associated with the pelvic plexus and hyogastric vessels, has been removed from the specimen.
- Ureter (retracted)
- Ductus deferens
- Coccyx (covered by fascia)
- Ampulla of ductus deferens
- Prostatic venous plexus, prostatic vein (uninjected and cut off)
- Seminal vesicle
- Ductus deferens
- Inferior vesical artery
- Levator ani muscle (covered by superior fascia of pelvic diaphragm)
- Obturator internus muscle (covered by obturator fascia)
- Obturator vein
- External iliac vein
- Obturator artery
- Lateral umbilical ligament
- Obturator nerve
- Upper pointer: Lateral puboprostatic ligament Lower pointer: Obturator canal
- Superior pubic ramus (pointer on pectineal ligament)
- Pubic branch of obturator artery
- Body of urinary bladder
- Superior vesical artery
- Longitudinal muscle of ureter extending into pubovesicalis muscle
- Superior vesical artery (branch communicating with artery of penis shown in 170-2, label no. 9)
- Cervix of bladder
- Pubovesicalis muscle
- Tendinous arch of pelvic fascia
- Puboprostatic ligament
- Dorsal vein of the penis
- Interpubic disc
- Body of pubic bone


