Bassett Collection of Stereoscopic Images of Human Anatomy
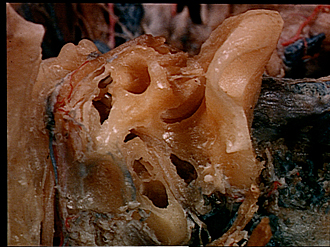
Dissection of left ear from posterior aspect
Relation of facial nerve and stapedius muscle to tympanic cavity and labyrinth
Image #62-5
KEYWORDS: Bones cartilage joints, Ear, Peripheral nervous system, Vasculature.
Creative Commons
Stanford holds the copyright to the David L. Bassett anatomical images and has assigned Creative Commons license Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International to all of the images.
For additional information regarding use and permissions, please contact the Medical History Center.
Dissection of left ear from posterior aspect
Relation of facial nerve and stapedius muscle to tympanic cavity and labyrinth
The semicircular canals have been cut away and the vestibule opened to show the footplate of the stapes (4) lying in the fenestra vestibuli. The facial nerve (7), together with branches of the stylomastoid artery and veins, is visible within the opened facial canal. The stapedius muscle and its nerve have been dissected and are illustrated to the drawing at 11. The muscle appears light in the view because of tendinous fibres on its surface. The tympanic branch (22) of the glossopharyngeal nerve (25) can be traced into the posterior part of the tympanic cavity.
- Greater superficial petrosal nerve
- Geniculate ganglion
- Vestibule
- Base of stapes in fenestra vestibuli
- Capitulum of malleus
- Body of incus
- Facial nerve (VII)
- Upper pointer: Posterior crus of stapes Lower pointer: Capitulum of stapes
- Pyramidal eminence
- Upper pointer: Manubrium of malleus Lower pointer: Tympanic membrane
- Stapedius nerve and muscle
- Tympanic sinus
- Mastoid cell
- Position of stylomastoid foramen
- Alar fascia
- Upper and lower divisions of vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) (vestibular part)
- Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) (cochlear part)
- Internal acoustic meatus
- Base of modiolus
- Veins surrounding internal carotid artery within carotid canal
- Osseous spiral lamina in basal turn of cochlea
- Tympanic nerve
- Mastoid cell
- Veins within petro-occipital fissure
- Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
- Vagus nerve (X)
- Anastomotic branch glossopharyngeal nerve with auricular brancjes of vagus nerve


