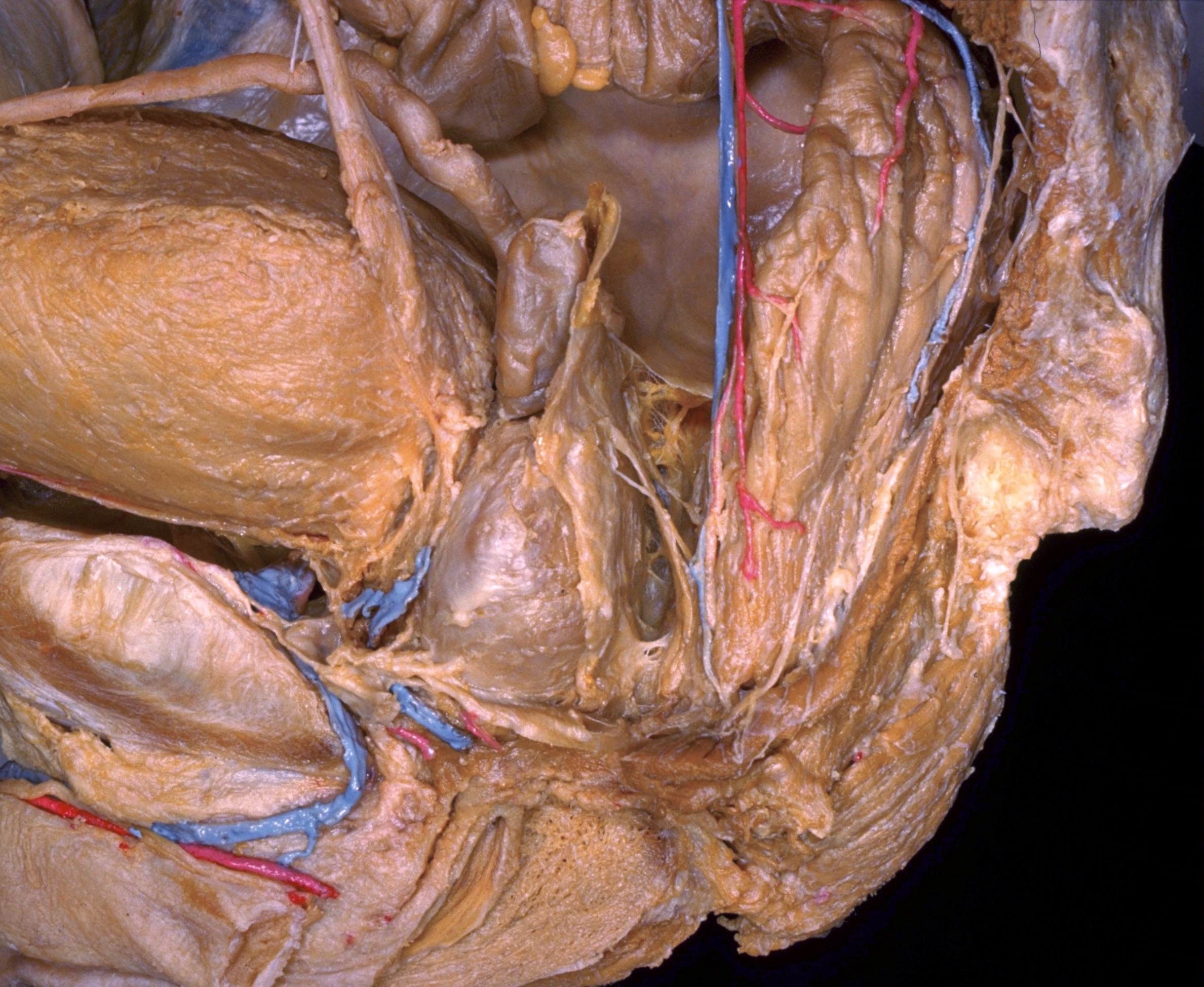
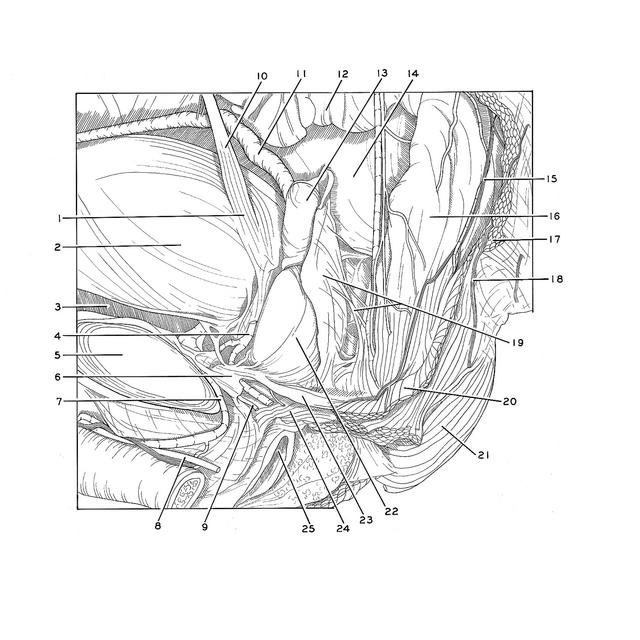
Dissection of male pelvis from a lateral approach
Prostate gland; puboprostatic ligament; rectovesical septum
Stanford holds the copyright to the David L. Bassett anatomical images and has assigned
Creative Commons license Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International to all of the images.
For additional information regarding use and permissions,
please contact Dr. Drew Bourn at dbourn@stanford.edu.
Image #170-2
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|