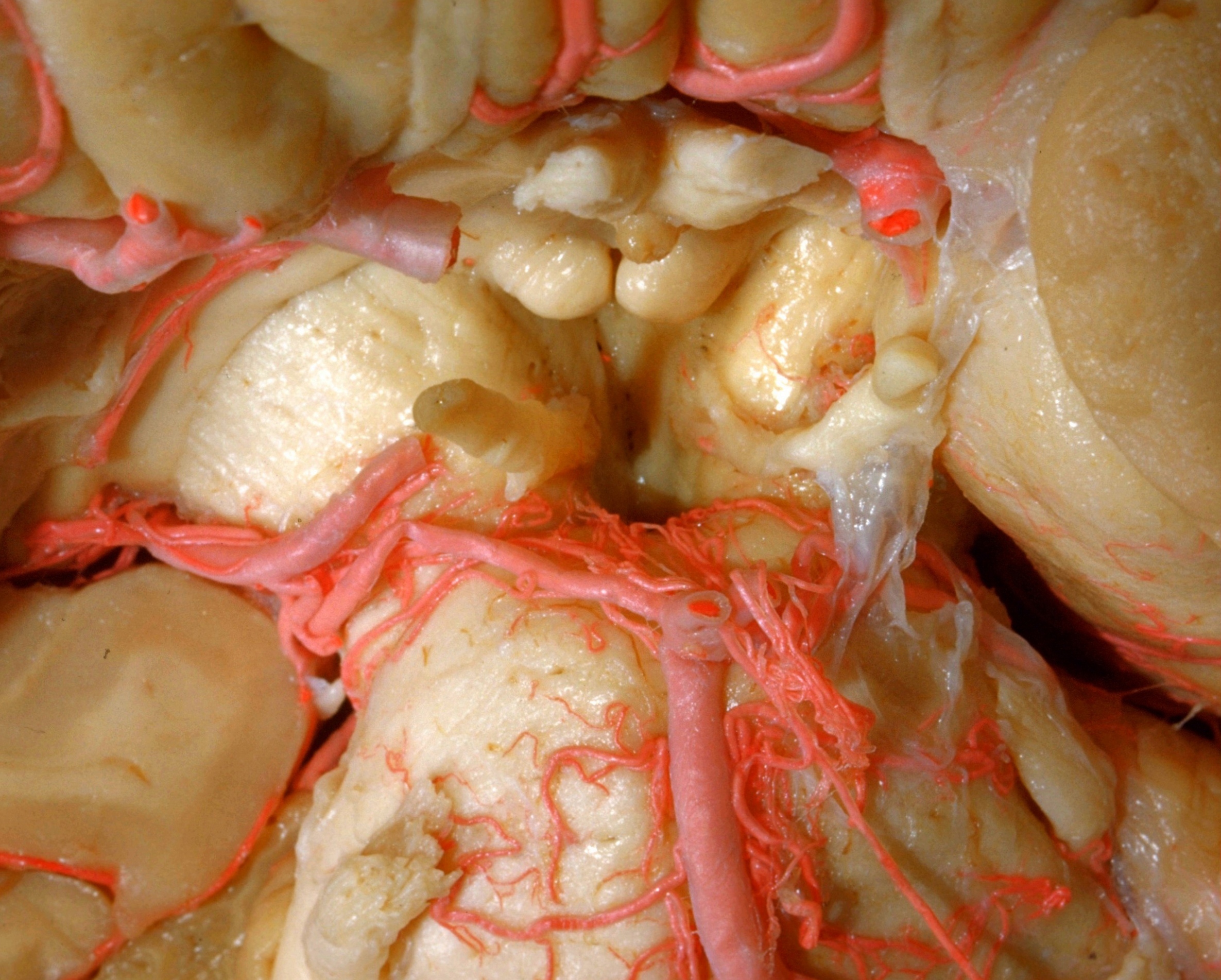
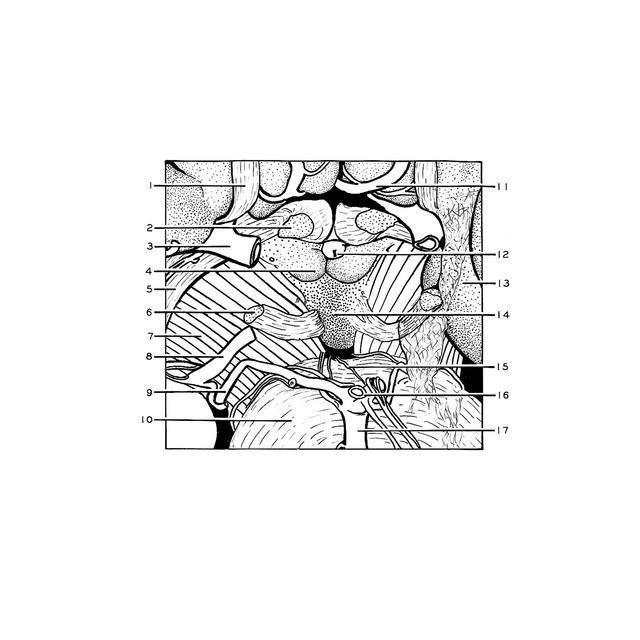
Exploration of the brain from its basal aspect
The posterior perforated substance and oculomotor nerves
Stanford holds the copyright to the David L. Bassett anatomical images and has assigned
Creative Commons license Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International to all of the images.
For additional information regarding use and permissions,
please contact Dr. Drew Bourn at dbourn@stanford.edu.
Image #4-7
 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|