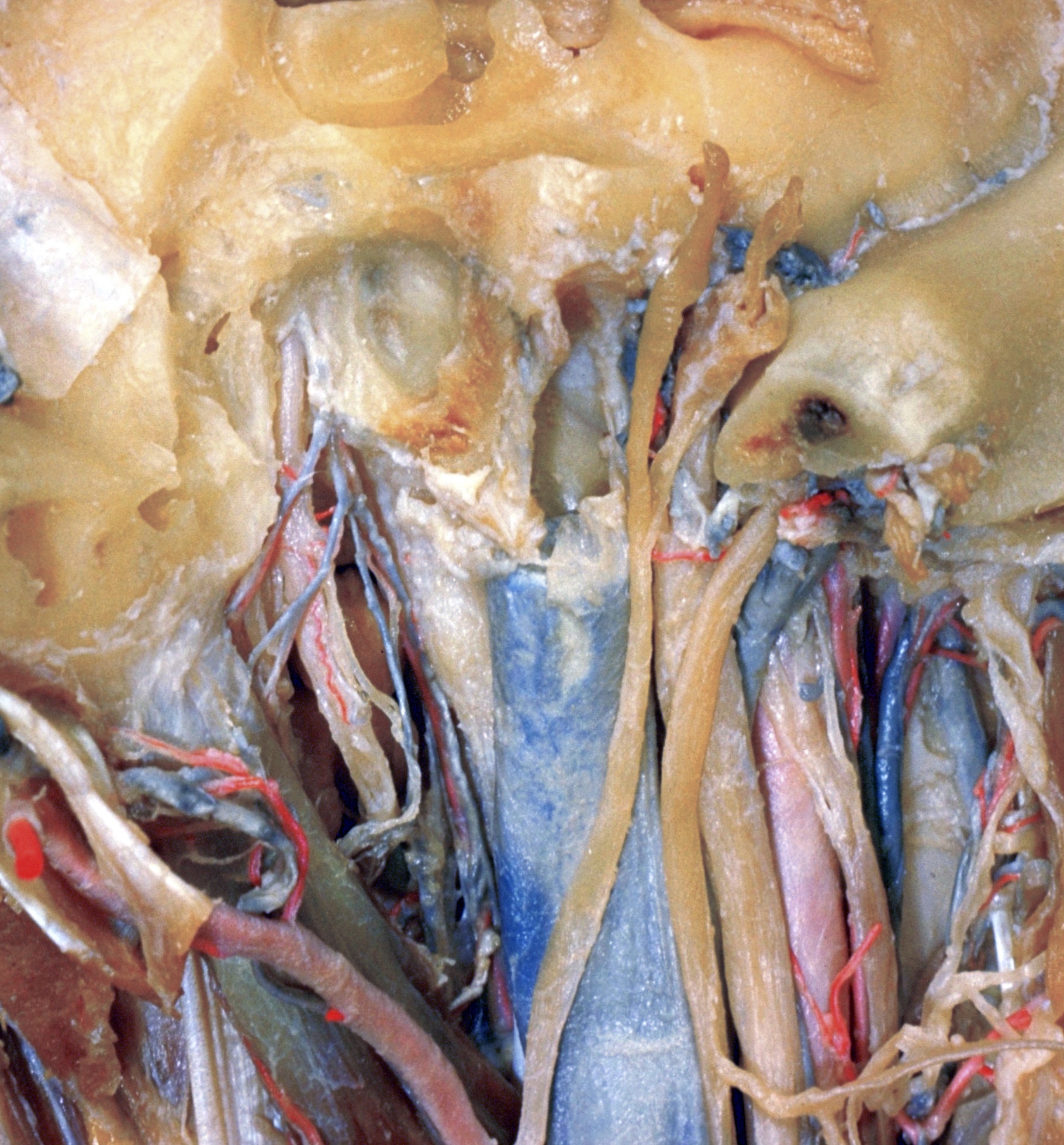
Dissection of head and neck from a posterior approach
Relations of facial, vagus, accessory, hypoglossal and internal carotid nerves; internal jugular vein
Stanford holds the copyright to the David L. Bassett anatomical images and has assigned
Creative Commons license Attribution-Share
Alike 4.0 International to all of the images.
For additional information regarding use and permissions,
please contact the Medical History Center.
Image #81-3

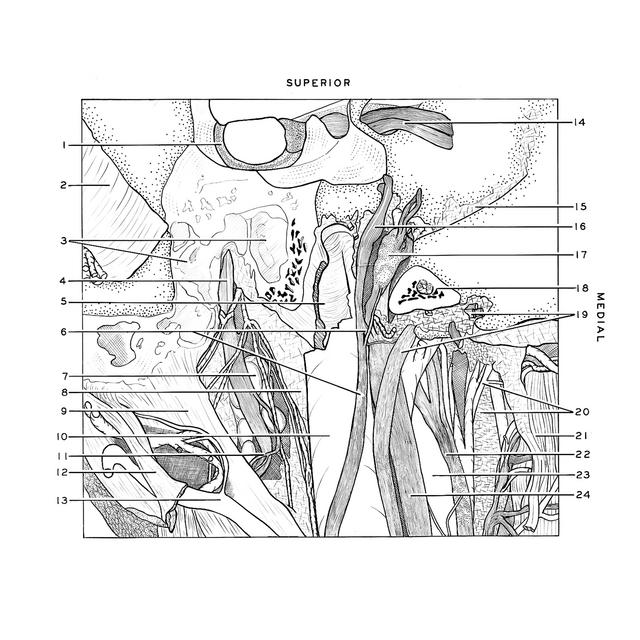

Dissection of head and neck from a posterior approach
Relations of facial, vagus, accessory, hypoglossal and internal carotid nerves; internal jugular vein
The accessory nerve has been reflected anteriorly to show its communication with the vagus nerve.
- Posterior semicircular canal
- Transverse sinus (sigmoid portion)
- Mastoid cells
- Facial nerve (VII) emerging from stylomastoid foramen
- Superior bulb of jugular vein (internal surface)
- Upper pointer: Internal branch accessory nerve Lower pointer: External branch accessory nerve
- Retromandibular process parotid gland
- Styloid process temporal bone (covered by periosteum)
- Posterior belly of digastric muscle
- Internal jugular vein
- Digastric branch of facial nerve
- Tendon of longissimus capitis muscle (cut across)
- Occipital artery
- Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
- Petro-occipital synchondrosis
- Accessory nerve (XI) (reflected anteriorly)
- Jugular ganglion of vagus nerve (X)
- Lateral part of occipital bone (cut across)
- Hypoglossal nerve (XII)
- Upper pointer: Ascending pharyngeal artery Lower pointer: Alar fascia
- Longus capitis muscle
- Internal carotid nerve
- Internal carotid artery
- Vagus nerve (X)